Risk management in the DIA Group
Start of main content
Risk management in the DIA Group
(102-11)
The DIA Group’s risk management model
The DIA Group has established a risk management model (hereinafter, “RMM”) with a systematic, detailed focus that allows it to identify, evaluate, and respond to risks related to the achievement of its business objectives.
This model, which is based on the COSO II Integrated Corporate Risk Management Framework COSO II (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission), ensures the identification of different types of risks (both financial and non-financial, such as operational, technological, social, environmental, and reputational risks).
The DIA Group’s RMM has a risk management policy which is applicable to the company and all of its subsidiaries, approved by the Group’s board of directors.
In the RMM application, DIA has contemplated all of its activities carried out in the different levels of the organisation, from the corporate level to those in the units and business processes, and are therefore applicable to the following levels: (i) execution of DIA’s strategy; (ii) achievement of the business objectives; and (iii) the proper execution of operations.
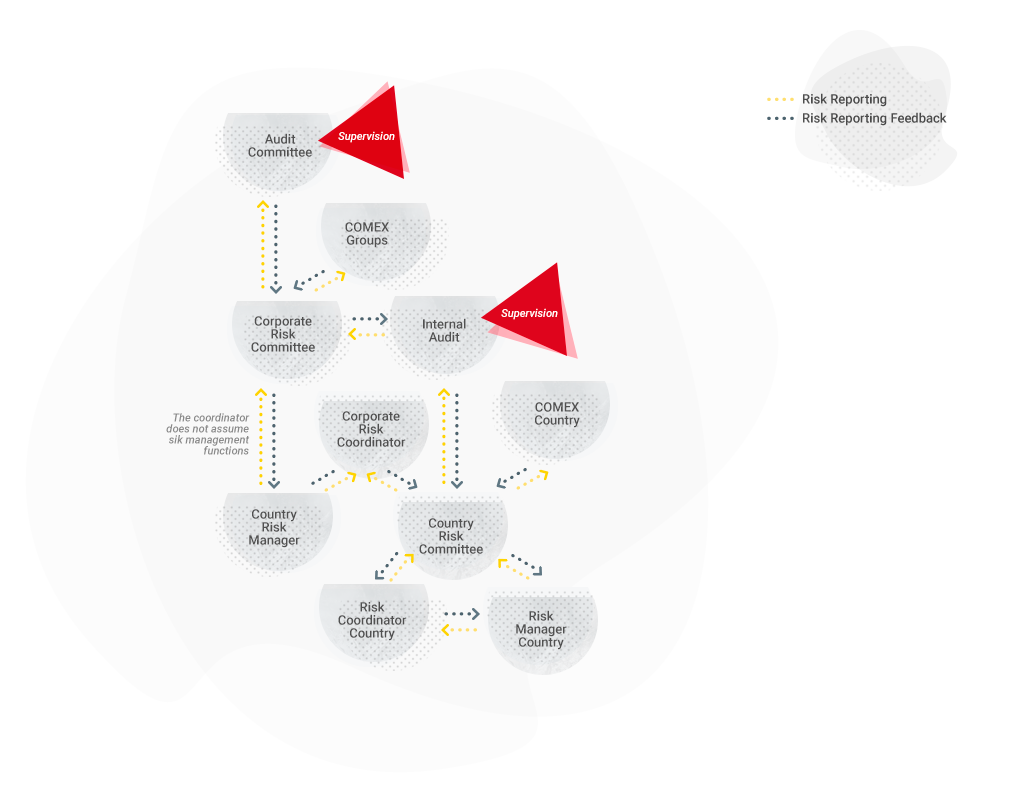
Organisational structure
The DIA Group’s Board of Directors, the Audit and Compliance Commission, and the Management Committee are responsible for ensuring the proper running of the RMM.
Main Responsibilities
Board of Directors
- Approval and setting of the risk control and management policy.
- Evaluation of the working quality and efficiency of the Board of Directors and the Commissions, approaching the risk management and supervision function as a key section.
Audit and Compliance Commission
- Supervision and periodic review of the Risk Management System
- Specific monitoring of the DIA Group’s financial risks.
- Supervision of the internal control systems of financial information.
- Supervision and periodic review of the efficiency of DIA’s internal control and internal audit procedures.
Management Committee
- Internal implementation of the RMM and creation of the strategy, culture, people, and technology that make up the RMM.
Corporate Risks Committee
- Analysis of the environment and new projects that can have a direct or indirect impact on DIA’s risks.
- Consideration of the inclusion of new risks and/or the disappearance of some of the existing risks.
- Recommendation of the development of specific action plans, monitoring planning, and continuity of existing plans.
- Continuous monitoring of key risks identified on the risk map, and in particular those that are closely related to DIA’s main interest groups, such as clients, franchisees, and suppliers.
- Evaluation and detailed analysis of DIA’s risks.
Internal Audit Department
- Review of the functioning of the risk control and management system, and the effectiveness of the control activities implemented.
Risk managers
- Continuous risk monitoring, through previously defined indicators.
Risk Management
Level of risk tolerance
DIA’s Executive Committee reviews DIA’s level of risk tolerance, which is presented to the Board of Directors to be reviewed and approved each year.
The risk valuation scales (probability and impact) are updated at least once a year, so that they can be adapted to the business strategy and circumstances. These valuation scales contemplate the different dimensions of the risk impact and likelihood of happening (financial, sales, operations, regulatory framework, human resources, and reputation) and allow the company to value the risks in each country and at the corporate level. These scales form the basis for the definition of the Group’s level of tolerance.
The DIA Group’s Risk Management Model defines tolerance as “the acceptable level of variation that DIA is prepared to accept in the achievement of its objectives”. This is therefore the maximum specific risk that the Organisation is prepared to take.
Main risks that can affect the achievement of business risks
The DIA Group’s main activity is the distribution of food, household, beauty and health products. In this context, the Group defines risk as any contingency, internal or external, which, if they materialise, would prevent or hamper the achievement of the objectives set by the organisation. Accordingly, it considers that a risk arises as a result of the loss of opportunities and/or strengths, as well as the materialisation and/or the strengthening of a weakness.
The main risks can be grouped into the following categories:
| Category | Main sources of risk | Main management / control mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental risks Risks and/or questions related to the environment in which the Group operates, including, among others, Political, Economic, Social, Technological, and Legal aspects. |
||
| Market / competition-related risks |
|
|
| Regulatory risks |
|
|
| Risks in the political and social context | Country risk | Development of research and periodic market/country surveys |
| Corporate Governance and Ethics Risks Risks and/or issues related with the corporate structure, the governance model, unethical irresponsible employee behaviour, or corporate social responsibility. |
||
| Corporate Social Responsibility |
|
|
| Integrity, fight against corruption and bribery, and reputation |
|
|
| Equity market risks | Conduct/practices that are contrary to the market | Internal Conduct Regulation in terms of Equity Markets |
| Operating Risks Risks and/or issues related to the Group’s business model and the execution of key activities in its value chain, including, among other areas, product quality and safety, the supply chain, environmental, health and security issues, human resources, and social or IT issues. |
||
| Product quality and safety |
|
|
| Environment |
|
|
| Issues related to social aspects, people, and Human Resources |
|
|
| Information systems |
|
|
| Financial Risks The Group’s activities are exposed to market, credit, and liquidity risks. For more details, see section 24 of the Management Report. |
||
The Group has a risk monitoring and updating system which allows it to identify and include in the company’s risk map any new risk that is identified, ensuring that all risks are reviewed at least once a year.
- Company structure and shareholder structure
- Corporate governance system
- Risk management in the DIA Group
- Compliance and ethics management in the DIA Group
End of main content



